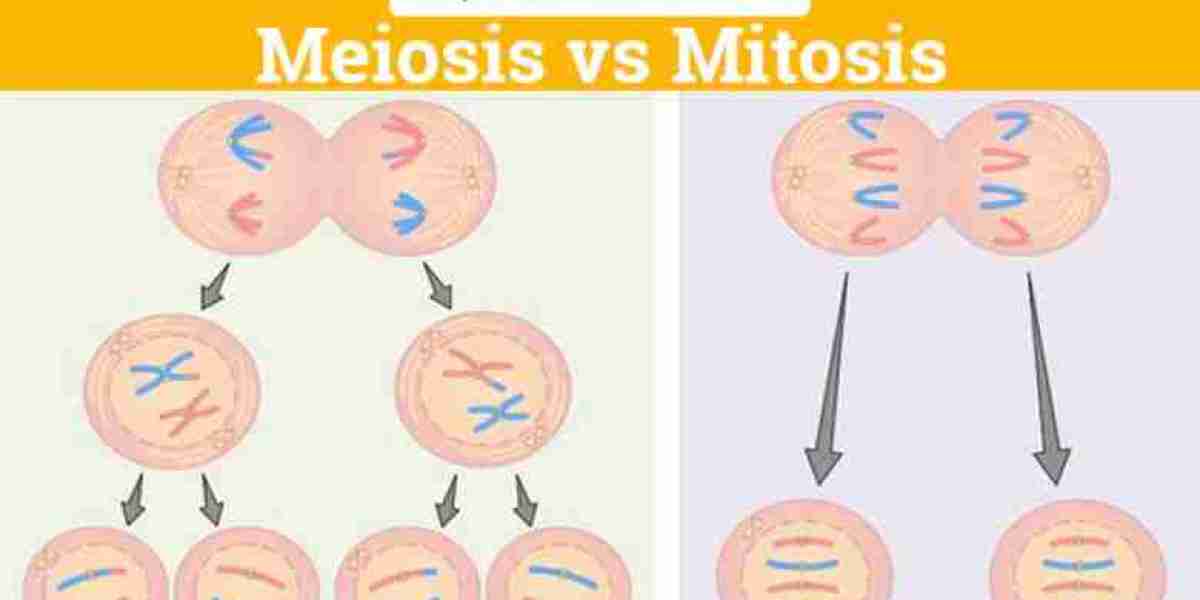
Mitosis and meiosis are two fundamental processes involved in the division and replication of cells, essential for growth, repair, and reproduction in living organisms. While both processes share similarities, they serve distinct purposes and exhibit unique characteristics. Let's explore the differences between mitosis vs meiosis to gain a deeper understanding of these vital biological phenomena.
Mitosis:
Mitosis is a process of cell division that occurs in somatic cells, leading to the production of two genetically identical daughter cells. It plays a crucial role in growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms. Mitosis consists of several distinct phases, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, each characterized by specific events such as chromosome condensation, alignment at the metaphase plate, separation of sister chromatids, and formation of new nuclei.
Key Features of Mitosis:
- Produces two daughter cells.
- Daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell.
- Occurs in somatic cells (non-reproductive cells).
- Essential for growth, development, and tissue repair.
- Involves a single round of cell division.
Meiosis:
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that occurs in germ cells, leading to the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This reduction in chromosome number is crucial for sexual reproduction, as it ensures that when gametes fuse during fertilization, the resulting zygote will have the correct chromosome number. Meiosis consists of two sequential divisions, known as meiosis I and meiosis II, each involving prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase stages.
Key Features of Meiosis:
- Produces four daughter cells.
- Daughter cells are genetically diverse due to genetic recombination and independent assortment.
- Occurs in germ cells (reproductive cells).
- Essential for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
- Involves two rounds of cell division.
Distinguishing Factors:
The primary differences between mitosis and meiosis lie in their outcomes, genetic content, and purpose. Mitosis results in the production of two identical daughter cells, while meiosis yields four genetically diverse daughter cells. Additionally, mitosis occurs in somatic cells for growth and repair, whereas meiosis occurs in germ cells for the production of gametes and the perpetuation of genetic diversity.
Conclusion:
In summary, mitosis and meiosis are two essential processes involved in cell division, each with distinct characteristics and purposes. While mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells for growth and repair, meiosis generates genetically diverse gametes for sexual reproduction. Understanding the differences between these processes is crucial for comprehending the complexities of cellular biology and the mechanisms underlying inheritance and genetic variation in living organisms.