Introduction:
Fibromyalgia is a chronic and complex medical condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and tenderness at specific points on the body. Despite being a relatively common disorder, fibromyalgia often poses diagnostic challenges due to its varied symptoms and the absence of definitive laboratory tests. In this comprehensive overview, we explore the intricacies of fibromyalgia, including its symptoms, diagnostic criteria, potential causes, and the impact on daily life.
pregabalin 75 mg capsules Can help in this types of pain.
- Symptoms of Fibromyalgia:
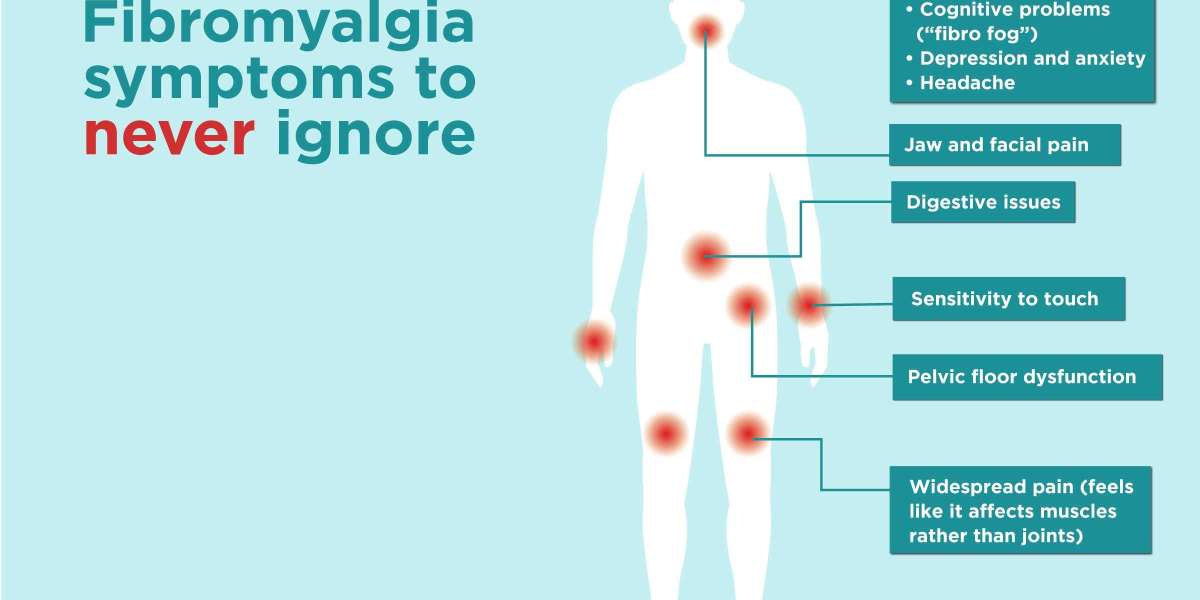
- Widespread Pain: The hallmark symptom of fibromyalgia is widespread pain that affects both sides of the body and is present above and below the waist. This pain is often described as a constant dull ache, but it can also manifest as shooting or burning sensations.
- Tender Points: Diagnosing fibromyalgia involves the identification of specific tender points on the body. These tender points, located at specific anatomical sites, are sensitive to pressure. Common locations include the neck, shoulders, chest, hips, and knees.
- Fatigue: Individuals with fibromyalgia often experience profound fatigue and a sense of unrefreshing sleep. Despite adequate rest, they may wake up feeling tired and exhausted.
- Sleep Disturbances: Sleep disorders, such as insomnia and restless legs syndrome, are prevalent among those with fibromyalgia. Disrupted sleep patterns contribute to fatigue and exacerbate other symptoms.
- Cognitive Symptoms: Termed "fibro fog," cognitive symptoms include difficulties with concentration, memory, and mental clarity. Individuals may struggle with tasks that require sustained attention or multitasking.
- Other Symptoms: Fibromyalgia can also be associated with headaches, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), jaw pain (TMJ), and heightened sensitivity to stimuli such as light, noise, and temperature.
- Diagnostic Challenges:
- Absence of Definitive Tests: Diagnosing fibromyalgia is primarily based on clinical evaluation, as there are no specific laboratory tests or imaging studies that definitively confirm the condition. Healthcare professionals rely on a combination of reported symptoms, medical history, and physical examination.
- Diagnostic Criteria: The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) has established diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia, which include the presence of widespread pain for at least three months and the identification of specific tender points. However, these criteria are not the sole determinants, and healthcare providers consider the overall clinical picture.
- Overlapping Symptoms: Fibromyalgia shares symptoms with other conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus. The overlapping nature of symptoms can complicate the diagnostic process, requiring thorough evaluation and exclusion of other potential causes.
- Potential Causes and Triggers:
- Central Sensitization: One prevailing theory suggests that fibromyalgia is related to central sensitization, wherein the nervous system becomes hypersensitive and amplifies pain signals. This heightened sensitivity to stimuli contributes to the widespread pain experienced by individuals with fibromyalgia.
- Genetic Predisposition: There is evidence to suggest a genetic predisposition to fibromyalgia, with a higher likelihood of the condition occurring in individuals with a family history of the disorder. Specific genetic factors associated with fibromyalgia are actively under investigation.
- Environmental Factors: Trauma, infections, and physical or emotional stressors are believed to play a role in triggering fibromyalgia in susceptible individuals. These environmental factors may contribute to the onset or exacerbation of symptoms.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalance: Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, have been implicated in fibromyalgia. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in regulating mood, pain perception, and sleep.
Understanding the potential causes and triggers of fibromyalgia is a complex and evolving aspect of research. As the scientific community delves deeper into the mechanisms of this condition, more targeted treatments and interventions may emerge.